Table of Contents
Advertising is a subsection of marketing, and marketing is a company's ability to profitably manage its customer base.
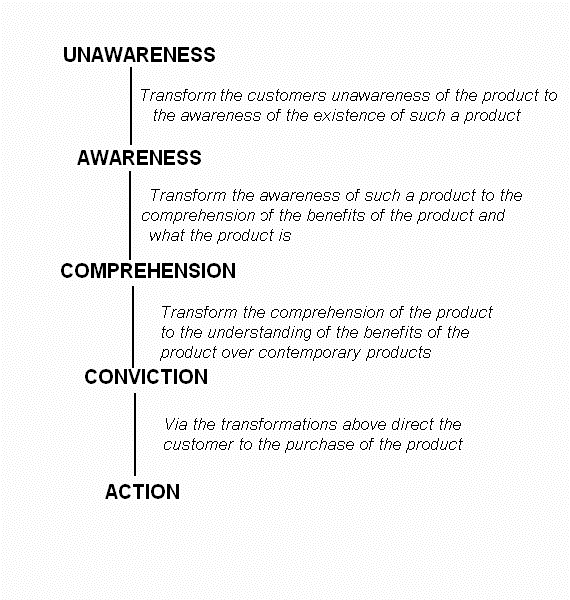
The advent of the Internet is causing the redevelopment of marketing strategies in all business. This unit covers an existing advertising strategy: DAGMAR — Defining Advertising Goals for Measured Advertising Results. This strategy attempts to move a customer from a state 'unawareness' concerning the product or service, to a state of 'action', in which it is hoped that the customer will buy the product. The four stages of DAGMAR are illustrated below:
A major marketing concerning facing the Internet is attracting customers to a website. In traditional media, such as the press and television, an audience is researched and targeted accordingly. Targeting via the Internet is difficult, but alternatives exist. For example, raising a site's search profile on the popular search engines such as Yahoo and Google, or by providing links to your site from Web pages most likely to be visited regularly by your target audience.
Once the target audience has been attracted, the website must explain, in a concise way, what the characteristics differentiating its featured product from that of its competitors are. Pictures might be used, as well as a list of its technical features and benefits.
Making claims about the product is, however, not sufficient. The audience must also be convinced that the claims are genuine. For instance, a lifetime guarantee could be given, or the claims could be backed with specific evidence.
The action stage does not necessarily involve a purchase. However, the customer may still want further information concerning the product, or even demonstration (this is very popular with software). This is often where failure occurs, due to difficulties in communication via the Internet.
To Do
Find out more about cybermarketing in your textbooks and on the Internet.
You need to ensure that the website has sufficient information for your potential customer to make an informed decision as to whether or not your advertised product or service is of interest. Over and above supplying information, the website should also persuade the customer that the product or company is indeed of interest.
Much effort and money can be invested in developing a large and complex website to advertise any particular product. However, if the product is not profitable, then those resources have been wasted. Alternatively, very little can be invested in developing a simple website. This runs the risk of offering smaller returns than a larger website would offer. Clearly, the cost for developing an appropriate website needs to be decided.
Software sells well on the Web, apples and oranges less so. However, the Web has a great deal of flexibility: it might be difficult to sell films on the Web, but a site listing theatre performances for the local theatre can be very useful, and might lead to more business.
Various experts sell their Web expertise, and they may be able to help with the design, implementation or maintenance of a website. Do you want to hire them, or do you want to develop the site yourself?
While a simple website requires little expertise, hiring an external company or independent contractor is probably beneficial for any medium-sized website. A large website may require employing new staff. In this case, all the work may be kept internal, or another company could be hired.
To Do
Go to the Interactive Advertising Bureau website. Here you will find a variety of interesting articles on Internet advertising.
There are many levels of advertising. A small company's Web site is likely less sophisticated and, for that matter, smaller than a large company's (such as General Motor's Web site — the URL is included at the bottom of the Contents section).
Different forms of information require different levels of sophistication in order to display it. Below is a list of information that could be provided on a website, ordered from 'least sophisticated' to 'most sophisticated'.
Contact information should be provided on any site. Supplying contact information allows a visitor to easily obtain more details concerning a product or service, if they so wish. Contact information should include the address of the company, the telephone number, and the name of the person to contact if appropriate. It may also include an email address.
The 'product' being advertised may be a specific item, such as a watch, or it may be a service, such as bookkeeping. Initial product descriptions should be limited, but as the site grows larger (assuming that it is successful), more product information should be included.
Further information can come in many forms: product specifications, testimonials, pictures and graphics showing the product or company offices, and so on. A site for the local library might include information about library events or stock additions.
Providing links to more information may encourage visitors to buy the product or service. This is a, essentially, a trust building exercise — if the site has something good to advertise, providing more information about can only increase the visitors' trust.
Many people use the Internet every day, but making them visit a particular website can be difficult. Appropriate visitors can more easily be found — and the site's hit rate hence improved — by using an HTML document's META tag.
The Web is available 24 hours a day and seven days a week. It is available all around the world. Every browser accessing the Web is a potential visitor and customer, and customers can visit a site at any time they find convenient, day or night.
An advertising billboard attracts the attention of many people, even those not interested in the product. It is seen only by those people in a particular area. People use the Internet to look for a particular product. If the product happens to be a product you are attempting to sell via a website, and the site can easily be found, it is much easier for your potential customers to find out about the product than via a billboard. A billboard may be said to be creating demand — the website is not creating demand, but instead making shopping easier for the customer.
The connection fees, hardware and software costs for setting up and running a website are minimal. Using an ISP (Internet Service Provider), running a simple website can cost under R100 per month. A Web server can be run on a standard PC, or, alternatively, free or commercial Web-hosting service can be used. As a result, many people have their own websites.
Collecting visitor data can generate useful information concerning customer interests and preferences. Collection can be done in a number of ways, for example: visitor actions can be recorded; visitors can be asked to fill in forms supplying information; their email addresses and interests can be recorded. Once this data has been collected, regular updates can be sent to customers using either email or physical mail, informing them of new products and further information.
It is important to keep customers happy, as well as to keep their interest on the website — sending a lot of unwanted mail, however, can damage this customer relationship.
To Do
Visit Search Engine Watch's tip page for submitting to search engines.
Read up about how businesses make use of the Internet to market their products and services.
When advertising software on a Web-site, the customer is always able to download and run a demonstration copy of the software. On the other hand, it is difficult to demonstrate the freshness and ripeness of any fruit or flowers, for example, that might be sold via a website. Showing a photograph of a mango does not let a customer examine the fruit in any way. Similarly, photographs of an automobile and a list of its specifications are informative, but customers are unable to drive the car. This problem can be lessened by supplying quality guarantees. Remember that the main goal of advertising is to catch the attention of possible customers, and hopefully a well-designed website will encourage them to seek further information, and possibly purchase the product or service.
The means to communicate emotions through non-verbal contact are limited, and therefore certain emotions that would be detected in person-to-person conversation are not easily detected in email or other textual information exchange. For instance, it is difficult to tell via email if a customer really is delighted to be investing a product.
When running a local business — a bakery, for instance — the benefits of advertising via the Web on the global market are lost. If the business is based in London, it does not matter if someone in New York City can see its website, because they cannot reach the shop to buy any goods.
If someone gains enough access to your site in order to edit its content, they will be able to negatively effect its advertising. For instance, Governmental sites have been broken into, and the Web pages have been changed to display pornography.
The competition can look at your site, see the listed prices, the available stock, and so on. Hence, a website provides competitors with easy intelligence. However, this is information that could probably be found elsewhere by any interested party, and so is not a major disadvantage.
It is important for a website itself to be advertised. Therefore, when building an informational website (as opposed to a commercial site), it is possible find funding by advertising other sites on your own.
Many larger websites have a large income from advertising other sites. This can be irritating to visitors, however, as they can easily be bombarded with a lot of (mostly) useless information.
Some ISPs, such as Geocities, provide free Web access. They can do this because, among other reasons, they advertise other products. This means that when one of the ISP's customers is browsing the Web they also see advertising placed there by that particular ISP.
An informational site about a particular area of interest often has people wanting the site to link to their sites, especially when they are selling a product related to the informational site's area of interest. These people could be charged in order to have such a link.
One factor to consider when advertising someone else's site is the quality of their product or service. You might want to only advertise what you consider to be good quality products. Showing their advertisement could be thought of as offering your seal of approval on their product.
People search the Internet for websites that interest them. The designer's job is to make it easy for them to find your site. The big search engines can easily have people visit at a site, provided the META tags are used appropriately. Also, linking to the site in as many places as possible and appropriate helps as well. There are a number of websites that act as central reference sources; these often link to other websites. It is important to have your site linked from all such appropriate centres. Some of these sites are:
The product website: When selling a product, it is very likely that there is already a general website for the kind of product you are selling. For example, when selling printers there is likely to be a general website for printers. Such a site may link to other sites that have information about printers, as well as to sites that sell printers. If there is such a site for your product, ensure that your site is listed here.
Some people predict that in the near future product Web sites will abound; they will be how people search the Internet.
The area website: If your website advertises a service or shop based in a particular location, then it is worth finding websites for the area as a whole. If such a site exists, then you want to be listed on it. Such area sites often link to local shops and amenities. For example, if your website is for a theatre in Islington, London, then your site should be linked to on Islington's website.
The interest group's Web site: A website that supports a group of people who share similar interests is an ideal place to link to your Web site, provided that you can identify an interest group matching your target audience. For instance, when building a site to advertise a series of painting exhibitions, link to the site from the home pages of local artist's.
Advertising another site is one way to fund your site.
Activity 1: Checking your site popularity
You can determine your site's popularity in many ways. We are going to illustrate these methods by using the the University of Cape Town's website.
The first method is to employ a ranking tool such as the one at Mike's Marketing Tools. Such a tool can be used to rank a site with respect to particular keywords. In the case of UCT, we can find its ranking with respect to the key word (or phrase) 'Cape Town': in other words, this is how high the UCT site ranks when people enter the phrase 'Cape Town' in a search engine. Of course, you could manually enter the phrase in all the search engines yourself, but these tools automate this process. Follow these steps:
Go to the Mike's Marketing Tools — Search Engine Rankings Tool.
Look for the 'Submission Form' section
In the URL enter www.uct.ac.za
In the keyword enter Cape Town
Submit the request by pressing the 'Check Rankings' button
Analyse the results and reflect on what they mean for the UCT website. Try key words and sites.
Another method is to determine the link popularity for the website. Link popularity refers to how often other pages link to the site's address. To do this using Google, do the following:
Visit Google and search for 'www.uct.ac.za'.
Google should return a page similar to the one below:
Click on the third option to search for pages that link to UCT. Google should return a list of results, and the number of results should give an idea of the site's popularity.
There is also a fourth option: finding pages that include the term 'www.uct.ac.za'. There should be significantly more websites that do this. Why do you think this is? Compare the results obtained from the previous search, and this one.
No matter how good a site is, it is useless unless people visit it. Here are some useful tips for attracting visitors to a site:
Add it to a "What's New" Web Page. Some sites maintain lists of new websites, in essence advertising these sites. These "What's New" pages tend to be viewed mostly by the more sophisticated user, which makes it less than ideal for attracting new customers.
Submit the site to a Web Directory, such as Yahoo or DMoz. Web directories are designed to help users find the sites they are looking for by browsing — rather than searching — the Internet.
Make the page searchable. Search engines automatically search documents and classify them, looking for information in the title, the top of the page, and in the HTML META tags. Pages can be made searchable by giving it a good title, putting appropriate keywords near the top of the page, and making use of the META tags.
Announce the site using Newsgroups, Newsletters, Books, and Magazines advertising sites.
Use lists of lists. These applications reference a site from hundreds of other sites. In many cases, these sites require sites that they link to to reciprocate, by advertising them in turn.
Activity 2: META Tags
Below is an example of a typical title and meta tag applied to a company, Cape Biscuits. The keywords used are biscuits, cookies and savouries.
<TITLE>Cape Biscuits CC.<TITLE> <META name="keywords" content="biscuits, savouries, cookies">
Design a website for a company that produces Crisps. The name of the company is, "The Crisp Factory". Choose a suitable title and keywords for the opening Web page.
Advertising is a sub-field of marketing. At the beginning of the section we examined a strategy based on the DAGMAR model, but we have not yet discussed this strategy in any detail with respect to the Internet. Below we return to three of the four transformations in the DAGMAR model. The fourth transformation, action, is left to the next section.
Product awareness can be improved by submitting a Web page to one of the major search engines, or by linking to the site from other Web pages popular with your target audience. Insert appropriate keywords in the META and TITLE HTML tags. Carefully chosen keywords can greatly enhance the likelihood of a page being identified by a particular search engine. One important method in keyword selection is to use synonyms. Synonyms can be found by performing a search with a given keyword and finding associated topics.
Awareness of a website can also be improved by linking from other popular websites, especially those with a similar topic area.
Product comprehension can be improved by providing detailed product information, statistics and / or scientific results. It is important, however, to allow the customer to choose how much information that they receive. It is possible to lose customers by inundating them with unwanted information.
Winning customer confidence can usually be best achieved by giving away samples. This often results in an 'action' (in the DAGMAR sense) from the customer's point of view, and might mean that the customer might never make it to the action of buying the product! There is a thin line between these two transformations: from Comprehension to Conviction, and from Conviction to Action. With software advertising, for example, demo software is often made available. This is good from the customer's point of view, since the demo gives them a much better understanding of the final product. This increases their confidence in the product. It is also healthy from the company's perspective as it allows them to receive important information about their customers, such as the networking domain they are attached to, employment and general demographics.
Exercise 1: Walt's Music Shop 1
Walt has several Music shops from which sells both new and used CDs and LPs. He began his career 20 years ago selling used LPs out of a small second floor room. After years of only scraping by and working very hard Walt expanded to three shops, all of which are in the same large metropolitan area (which we will call Metropolis).
The MP3 hype on the Web has made Walt interested in computers. He's bought a computer, and he and a few of his employees are now avid Web surfers.
Walt wants to do some advertising on the Web. He's thought about selling items on-line, but has decided, at least for now, only to advertise. Do you think Walt is wise to advertise on the Web? Write approximately 150 words justifying your answer and suggesting how Walt could use his site to support his business. Write your response as if you were addressing Walt himself.
Read Discussion of Exercise 1 at the end of the Unit.
Exercise 2: Walt's Music Shop 2
Walt is convinced by your answer. Realising that you are something of an expert in this area, he asks what you think he should put on his site.
Walt does not have much of an advertising budget and is unsure how much this site would cost. Provide him with three options: one for an inexpensive site, another for a slightly more expensive site, and finally one for a full-blown, highly interactive website. Which one would you recommend?
Read Discussion of Exercise 2 at the end of the Unit.